Summary
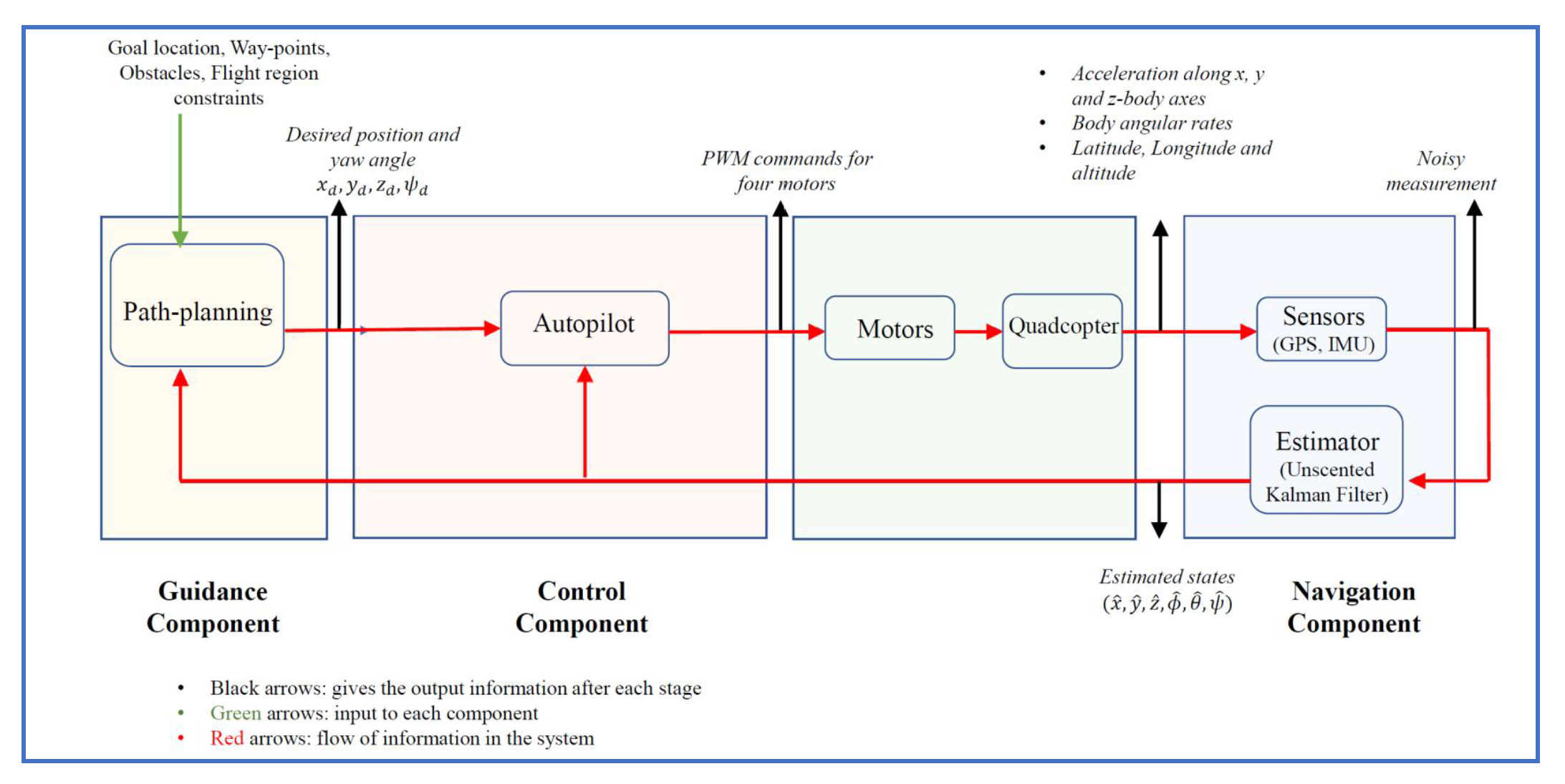
The guidance, navigation and control (GNC) subsystem is designed for the quadcopter for autonomous flight and waypoint navigation with obstacle avoidance. The navigation for the UAV is carried out using the sensors and an estimator. Inertial measurement unit (IMU) (with gyroscope and accelerometer) and GPS are considered as the sensors to obtain the measurements during the flight. The gyroscope provides the angular-rate information (roll rate, pitch rate and yaw rate) of the UAV, the accelerometer provides the acceleration measurements along the x, y, and z body axes of the system, and the GPS provides the latitude, longitude and altitude information of the UAV. The measurement outputs from these sensors are generally noisy. Unscented Kalman filter (UKF) is considered as the estimator to extract the estimates of the states of the UAV from the obtained measurements. The guidance component intakes the estimates of the inertial position and the body-fixed orientation angles from the navigation component. Further, the goal location, location of waypoints and location of stationary obstacles are fed to the guidance component of the GNC subsystem. Based on the known locations of stationary obstacles, waypoints and goal, path-planning is carried out using the rapidly-exploring random tree (RRT*) algorithm. A position controller is designed to obtain the desired roll and pitch angles based upon the desired position locations obtained from the guidance component. For the given desired roll and pitch angles from the position controller and desired yaw angle from the guidance component, the roll, pitch and yaw moments as inputs are designed using Proportional-integral (PI)-based attitude controller. Finally, to detect, localize and classify the shape, color, and alphanumeric character of the object, a convolution neural network (CNN)-based algorithm called YOLO (You Only Look Once) is adapted.